🔹 Introduction
If
you are running a business in India, filing GSTR‑1
is one of the most important GST compliances you cannot ignore. Whether you are
a small trader, manufacturer, or SME, GSTR‑1 ensures
your sales data is correctly reported to the GST system. Errors or delays can
lead to penalties, notices, or blocked Input Tax Credit (ITC) for your
buyers.
In
this guide, we’ll cover: -
·
What
is GSTR‑1
·
who
should file it
·
Due
dates (monthly & quarterly)
·
Step‑by‑step process
to file GSTR‑1
online
·
Common
mistakes to avoid
·
Penalties
for late filing
·
FAQs
for easy understanding
(References:
Section 37 of CGST Act, 2017 & Rule 59 of CGST Rules, 2017)
🔹 What is GSTR‑1?
GSTR‑1
is a monthly/quarterly return that contains details of all outward
supplies (sales) made by a registered taxpayer.
·
It
includes B2B, B2C, exports, and exempt supplies etc.
· Once
you file GSTR‑1,
the details flow automatically to the buyer’s
GSTR‑2B,
enabling ITC.
👉
Simply put, GSTR‑1
= Your sales report to GST Department.
Legal
Reference: Section 37(1) of CGST Act –
Every registered person (except composition taxpayers, ISD, TDS/TCS deductors)
shall furnish details of outward supplies in GSTR-1.
🔹 Who Should File GSTR‑1?
·
All
regular taxpayers registered under GST.
·
Casual
taxable persons.
·
SEZ
units and developers.
·
Exporters.
❌ Exempted:
Composition scheme taxpayers (they file CMP‑08
instead).
🔹 GSTR‑1
Due Dates in 2025
|
Filing Type |
Turnover |
Frequency |
Due Date |
|
Monthly GSTR‑1 |
> ₹5
crore |
Monthly |
11th of next month |
|
Quarterly GSTR‑1
(QRMP) |
≤ ₹5
crore |
Quarterly |
13th of month following quarter |
⚠️
Missing the due date results in late fee + interest (Sec. 47).
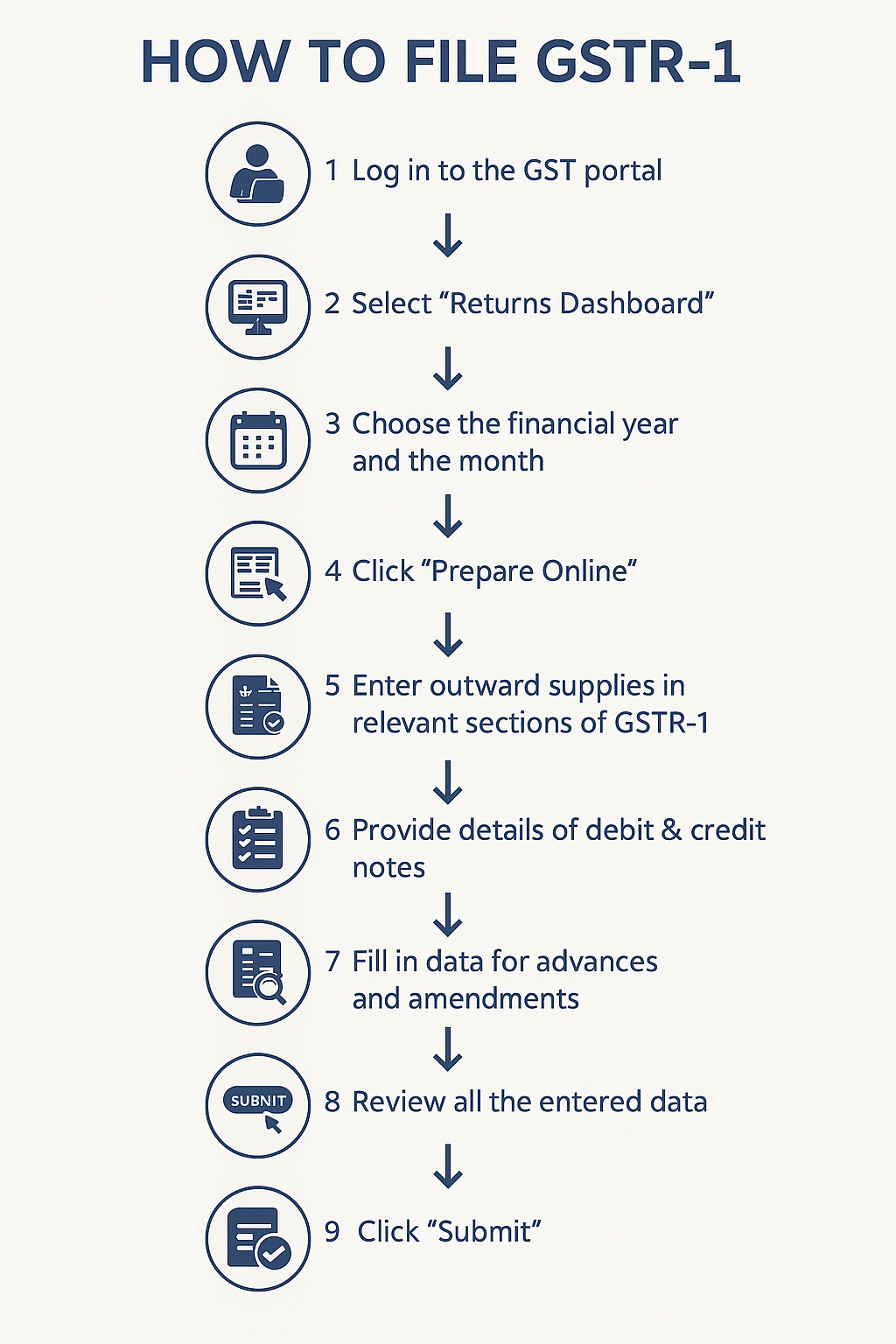
🔹
Step‑by‑Step Process to File
GSTR‑1 Online
Step
1: Login to GST Portal.
Step 2: Go to Returns Dashboard → Select period.
Step 3: Click Prepare Online under GSTR‑1.
Step 4: Enter details:
·
B2B
Invoices (GSTIN of buyers, taxable value, tax rate)
·
B2C
Large (value > ₹2.5 lakh interstate)
·
B2C
Small (consolidated)
·
Exports
(with/without payment of tax)
·
Credit/Debit
Notes
Step 5: Save, Preview & Submit.
Step 6: File using DSC/EVC.
Step 7: ARN generated → Acknowledgement of filing.
🔹
Common Mistakes in GSTR‑1 Filing
·
Wrong
GSTIN entry for buyers → Buyer loses ITC.
·
Mismatch
between GSTR‑1 vs GSTR‑3B.
·
Missing
export invoices.
·
Not
reporting credit/debit notes.
·
Filing
late → attracts penalties.
🔹
Penalties for Late Filing (Sec. 47)
·
Late
Fee: ₹50 per day (₹25 CGST + ₹25 SGST).
·
Nil
Return Late Fee: ₹20 per day (₹10 CGST + ₹10 SGST).
·
Max
Cap: ₹5,000 per return.
·
Interest: 18% p.a. on tax liability (if
any).
👉 Delay also blocks your buyer’s
ITC claim → impacts business relations.
🔹 FAQs on GSTR‑1
Q1. Can I
revise GSTR‑1?
No direct revision option. Corrections can be made in the next return or
amended GSTR-1 can be filed.
Q2. What if I don’t file GSTR‑1?
You cannot file GSTR‑3B
until GSTR‑1
is filed. Notices may be issued.
Q3. Can I file NIL GSTR‑1?
Yes, if no outward supplies in a period → file NIL GSTR‑1.
Q4. What is IFF in QRMP scheme?
Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) lets quarterly filers upload monthly B2B
invoices.
🔹 Conclusion
Filing GSTR‑1 accurately and on time is crucial for compliance,
avoiding penalties, and ensuring your buyers can claim ITC smoothly. With the
right process and checklist, SMEs and traders can file hassle‑free.
📌 Need help with GSTR‑1 filing or facing GST notice issues?
Contact TechTax – Your Trusted GST Partner in Ghaziabad, Noida & Delhi.